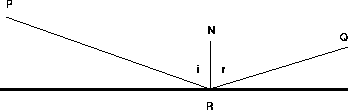
Figure 27.1: Snell's law, Angle of Incidence, i=r, Angle of Reflection
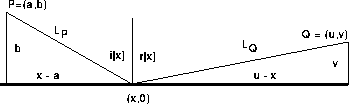
Snell's law from optics says that light traveling from point P to point Q reflects off a mirror so that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. This is illustrated in Figure 27.1. The angle of incidence is i between the incoming ray of light and the normal to the mirror. The angle of reflection is r between the normal and the outgoing ray of light.

Fermat gave a more general variational principle governing the path of light. Fermat's principle says that light travels along the path that requires the least time. Among all paths reflected off a flat mirror, we can see geometrically that light will reflect at the point where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. In other words, Fermat's principle implies Snell's law.
To show that Fermat's principle gives Snell's law, suppose light reflected at a different point S on the mirror. We will show that the time required for light to travel from P to Q through S is more than the time required to travel from P to Q through R, where i=r as shown in Figure 27.1.
Construct the point P' an equal distance below the mirror on a line normal to the mirror. Since the angles i and r are equal, the points P', R, and Q lie on a line. By similar triangles, the distance traveled by light going from P to R is the same as that traveled by light going from P' to R, so the distance traveled from P to R to Q is the length of P'Q.
The distance traveled by light going from P to S is the same as that traveled by light going from P' to S by similar triangles, so the distance traveled by light going from P to S and then to Q is the sum of the two lengths P'S plus SQ. Since these segments form the sides of a triangle with P'Q as a base, P'S+SQ>P'Q. In other words, P to R to Q is the shortest reflected path.
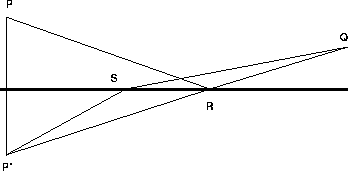
Finally, light travels at constant speed c in air, so the shortest path is fastest and Fermat's principle says light must reflect at the point R that makes i=r. In other words, Fermat's principle implies Snell's law.
Before we move on to study reflection off curved mirrors, it is worthwhile to give a calculus proof of the shortest path. We need to formulate the problem analytically.
 Snell by Calculus
Snell by Calculus
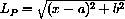 .
2) Use the Pythagorean theorem to show that the length of the line segment from (x,0) to (u,v) is
.
2) Use the Pythagorean theorem to show that the length of the line segment from (x,0) to (u,v) is
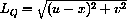 .
3) Light travels at speed c, so the time required for light to go from (a,b) to (x,0) is the distance over c. Similarly, the time required to go from (x,0) to (u,v) is that distance over c. Show that the total time required for a ray of light to travel this path is
.
3) Light travels at speed c, so the time required for light to go from (a,b) to (x,0) is the distance over c. Similarly, the time required to go from (x,0) to (u,v) is that distance over c. Show that the total time required for a ray of light to travel this path is
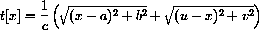
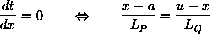

27.1
Now we reflect light off a curved mirror.
For simplicity, we assume that the mirror is in the shape of a graph y=f[x]. A light ray hitting the graph at (x,f[x]) is shown in Figure 27.5.
The length
To minimize t[x], we begin by computing critical points,
In order to easily interpret this formula, we need the fact that the cosine of the angle between two vectors
You can study this formula in Chapter 15 of the text, or just use it now.
Applying this formula to the angles between the tangent vector
If the incoming light ray is vertical,
Problem 27.1
Figure 27.19 is a comparison of rays of light reflected off different mirrors.
Problem 27.2
A sphere does not focus vertical rays to a point; it only focuses to a dark spot known as a caustic.
What does an ellipse do? A sinusoid?
Problem 27.3
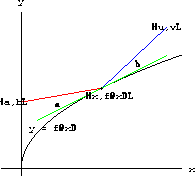
Figure 27.4: Reflection off y=f[x] 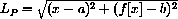 and the length
and the length
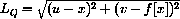 (by the length formula or Pythagorean theorem), so the time required for light to pass along the path is
(by the length formula or Pythagorean theorem), so the time required for light to pass along the path is
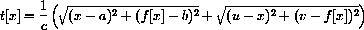
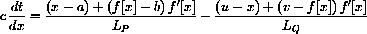
so that critical points satisfy
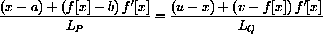

is given by the simple formula
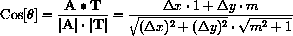
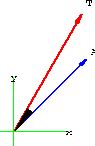
Figure 27.5: The angle between
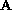 and
and
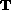 .
. 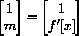 and each of the vectors from P to (x,f[x]),
and each of the vectors from P to (x,f[x]), 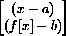 , and (x,f[x]) to Q,
, and (x,f[x]) to Q, 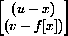 , gives the cosines of the angles,
, gives the cosines of the angles,

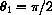 , then
, then
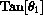 is undefined.
The ray is perfectly OK, but the math breaks down.
is undefined.
The ray is perfectly OK, but the math breaks down.
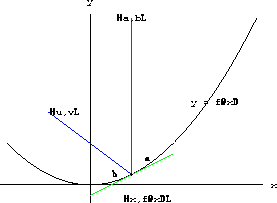
Figure 27.10: Vertical Incoming Light
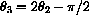 for vertical incoming light reflecting off the curve y=f[x] whose tangent line makes the angle
for vertical incoming light reflecting off the curve y=f[x] whose tangent line makes the angle
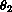 with the vertical.
with the vertical.
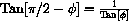 .
.
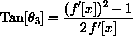
Use the formulas you obtained above to make computer programs that reflect a whole table of lines.
For example, you might input a list of vertical lines beginning at (x,10) and hitting the graph y=f[x] at (x,f[x]) for a list of x's. Each line in your input list generates a reflected line from your formula.
Make reflections for several functions.
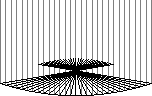
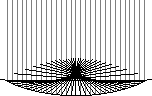
Prove that vertical rays reflected off a parabola all intersect at the "focus" point of the parabola.
A student discovered in his project that a sine curve nearly reflects light to a point.
Can you think of a reason by using Taylor's formula from the Mathematical Background?